The 3D spatial data processing group had the opportunity to collaborate with the team of Prof. Tzu-Ping Lin from National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan, within the frame of a study dealing with carbon emission reduction measures in urban environments.
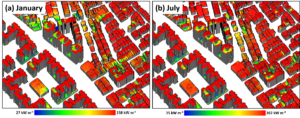
One option of reducing carbon emission by buildings is to install photovoltaic (PV) panels in order to meet the energy needs of buildings. The Voxel Octree Solar Toolkit (VOSTOK), which is developed at the 3D spatial data processing group, was applied in order to calculate estimates of solar potential on the roofs in various urban structures.
Main advantages of VOSTOK are its ability to take into account mutual shading between buildings, and the free choice of temporal resolution. Subsequently, a seasonal carbon budget on a monthly basis is provided in the study, leading to recommendations such as the installation of PV in areas with homogeneous building height distribution.
Check out the manuscript for a detailed description of the study:
Tzu-Ping Lin, Feng-Yi Lin, Pei-Ru Wu, Martin Hämmerle, Bernhard Höfle, Sebastian Bechtold, Ruey-Lung Hwang, Yu-Cheng Chen, Multiscale analysis and reduction measures of urban carbon dioxide budget based on building energy consumption, Energy and Buildings, Volume 153, 2017, Pages 356-367, ISSN 0378-7788, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.07.084.