Category: Publications
-
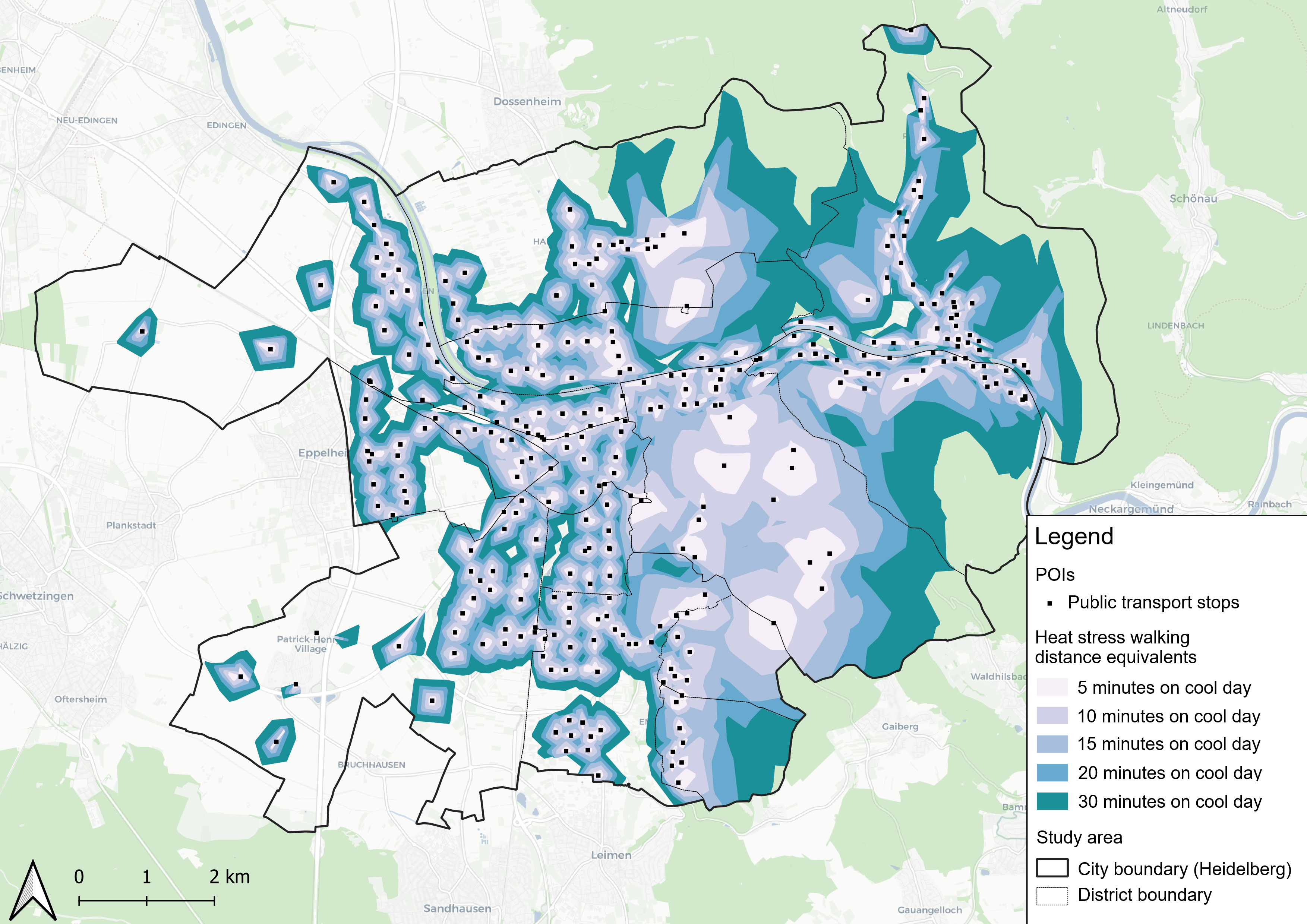
New Paper “Accessibility for pedestrians under heat stress – the example of Heidelberg, Germany”
This study introduces the isocalor approach to assess how solar exposure and heat stress impact pedestrian access to essential services in Heidelberg, using OpenStreetMap data and a customized openrouteservice routing engine. As climate change intensifies, cities are increasingly exposed to extreme heat events, with urban populations—especially vulnerable groups like older adults, children, and those with…
-
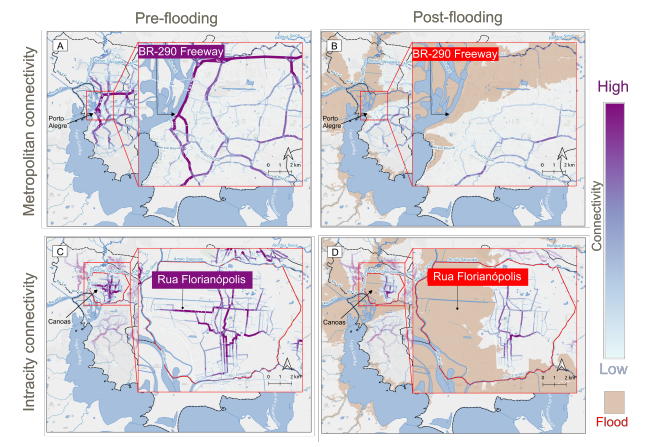
New paper “Changes in Road Centrality and Hospital Access Redundancy: Impacts of the 2024 Flood in the Metropolitan Core of Porto Alegre”
This study examines the resilience of urban infrastructure, with a focus on road network connectivity and redundancy in the face of extreme weather events. Using OpenStreetMap (OSM) data and the openrouteservice (ORS) routing engine, the research assesses centrality metrics and redundancy to evaluate how floods impact mobility and access to critical services, such as healthcare.…
-

3DGeo April Recap: Conferences
It was an exciting month for the 3DGeo research group in April. Three major conferences took place: Let’s give you some impressions below! JISDM The Joint International Symposium on Deformation Monitoring (JISDM) brings together experts on deformation monitoring from a range of fields such as photogrammetry, remote sensing and of course geodesy. It is a…
-
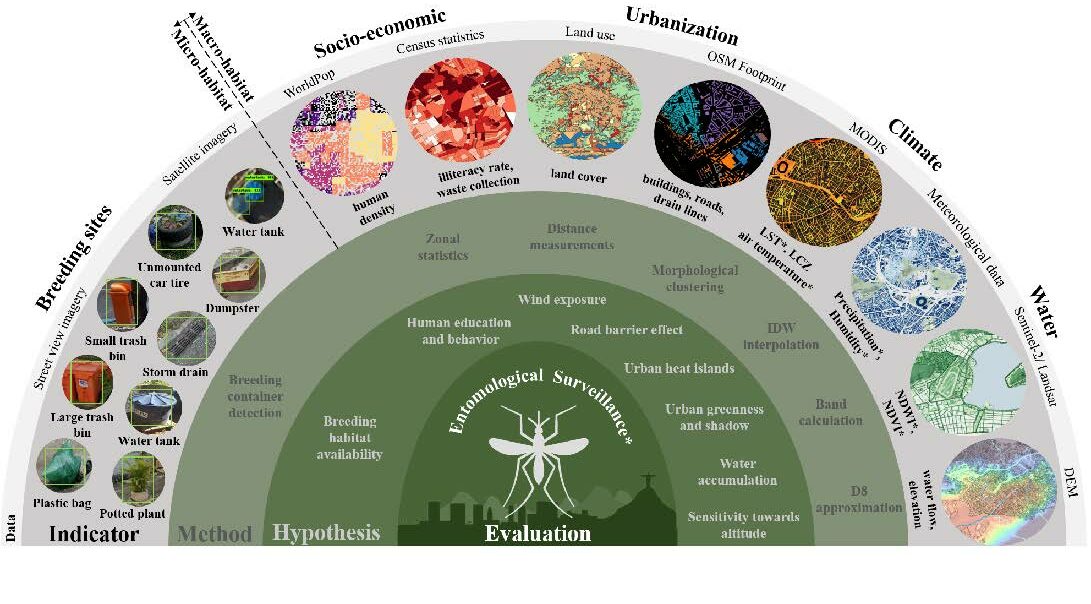
New Paper in Lancet Planetary Health “Urban Aedes aegypti suitability indicators”
To improve vector control strategies, Dr. Steffen Knoblauch (PostDoc at GIScience and HeiGIT) has developed detailed maps showing where Aedes aegyti is most likely to thrive. Using a holistic approach, his work leverages geospatial big data – including openly available satellite and street view imagery as well as climate data – to identify common breeding…
-
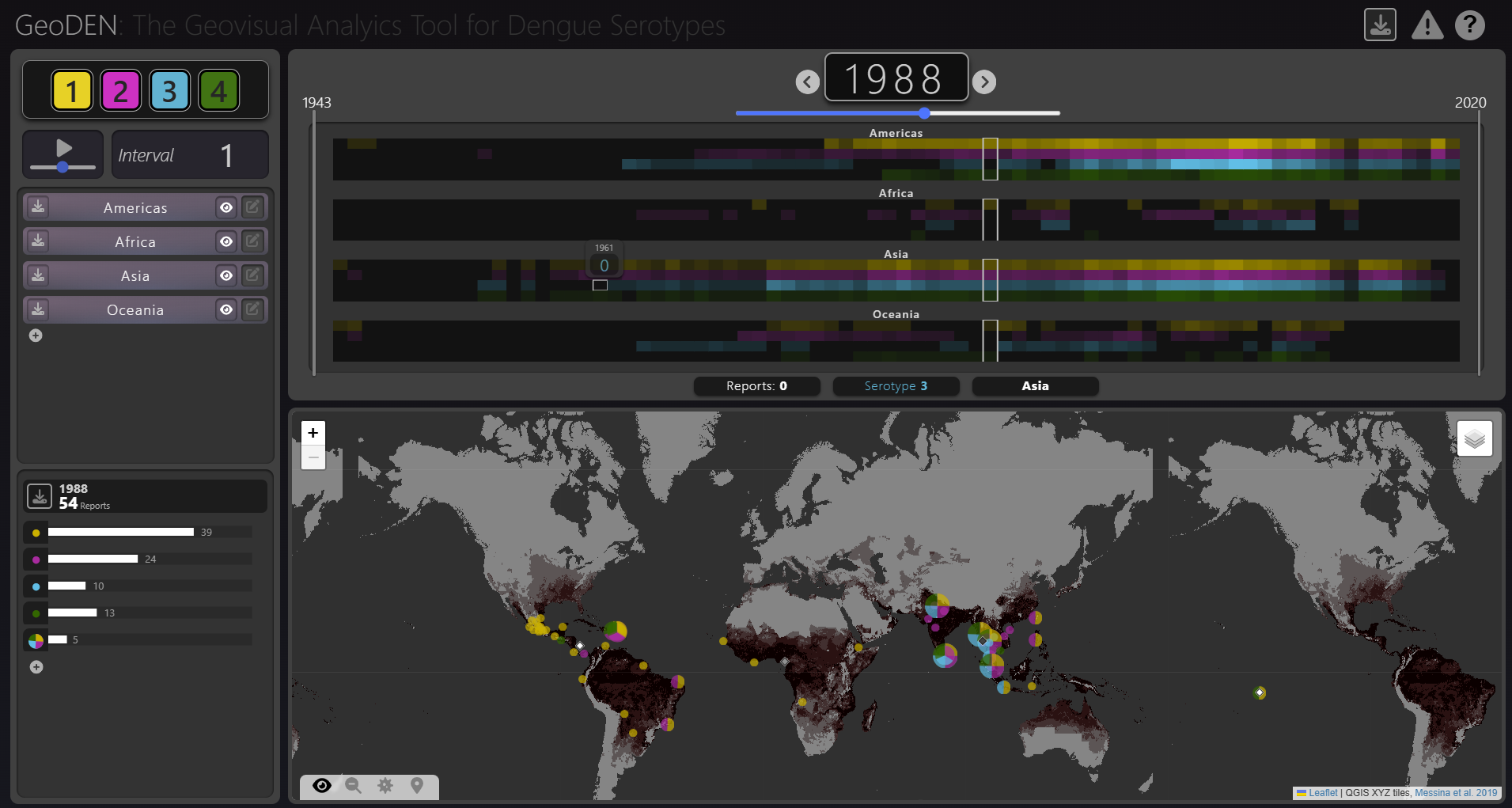
New Paper “GeoDEN: A Visual Exploration Tool for Analyzing the Geographic Spread of Dengue Serotypes”
With the increasing availability of global disease datasets, Visual Analytics (VA) has emerged as a valuable tool in spatial epidemiology, particularly for studying serotype interactions in diseases like dengue. Dengue, caused by four serotypes (DENV1-DENV4), poses a significant global health threat exacerbated by urbanization and climate change. Traditional approaches rely on static mapping or animation…
-
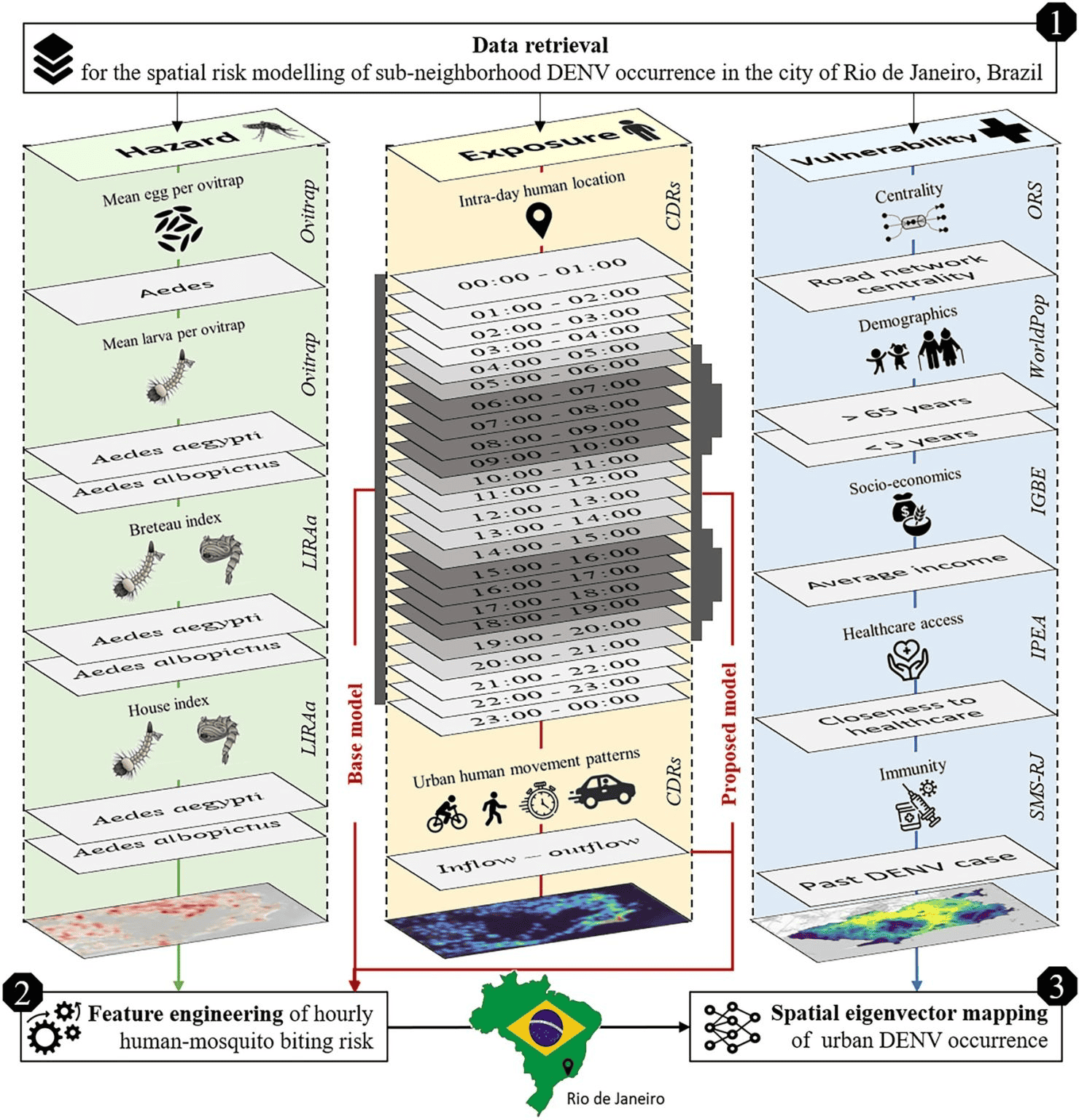
New Paper in Scientific Reports “Modeling Intraday Aedes-human exposure dynamics enhances dengue risk prediction”
Scientific Reports publishes a paper by Steffen Knoblauch et al. that underscores the critical importance of integrating vector ecology and human behavior into advanced disease modeling frameworks. The increasing availability of human movement data presents significant potential for tackling global public health challenges, especially in the context of infectious diseases. This is particularly important for…
-
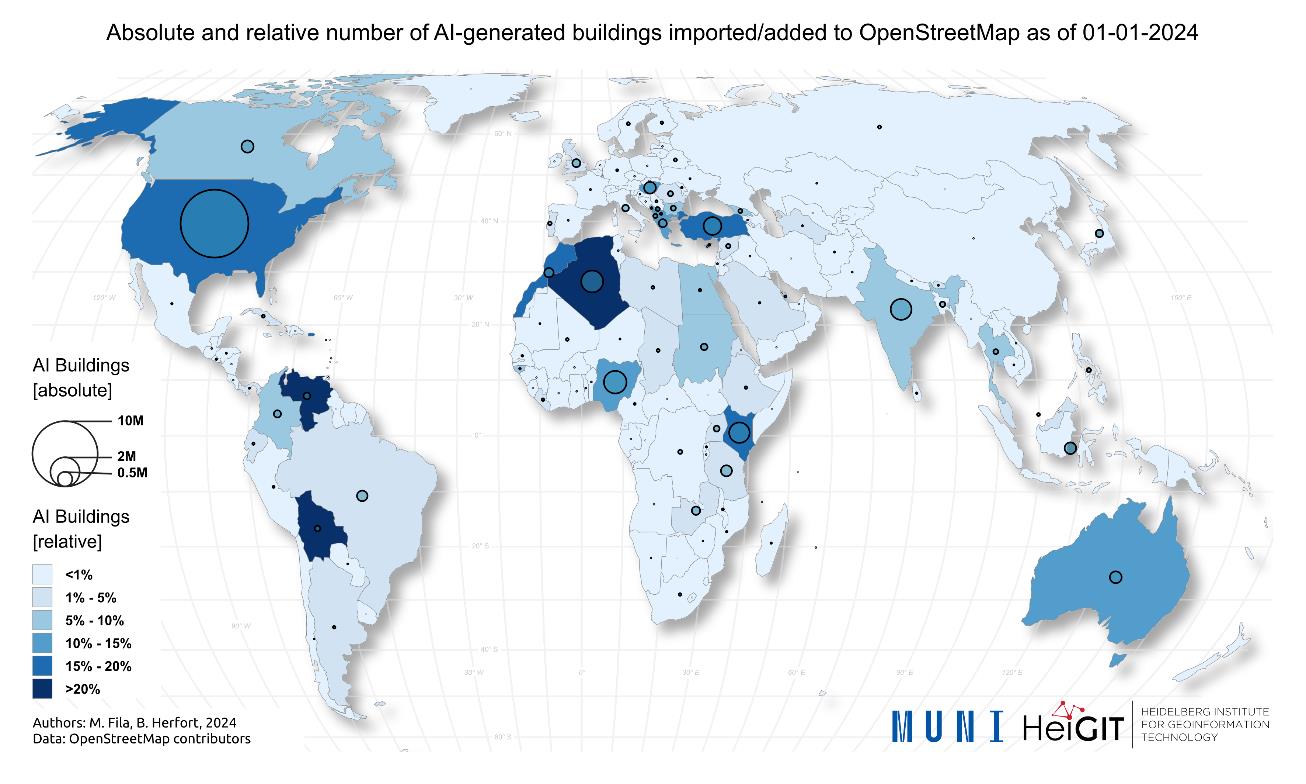
New Paper “AI-Generated Buildings in OpenStreetMap: Frequency of Use and Differences from Non-AI-Generated Buildings”
The concept of a “Digital Earth” has long envisioned a future where technological advancements enable the large-scale collection and visualization of spatial and environmental data. Today, open data sources such as OpenStreetMap (OSM) provide crucial spatial information for diverse applications, including urban planning, disaster management, and public health. However, many regions remain insufficiently mapped, particularly…
-
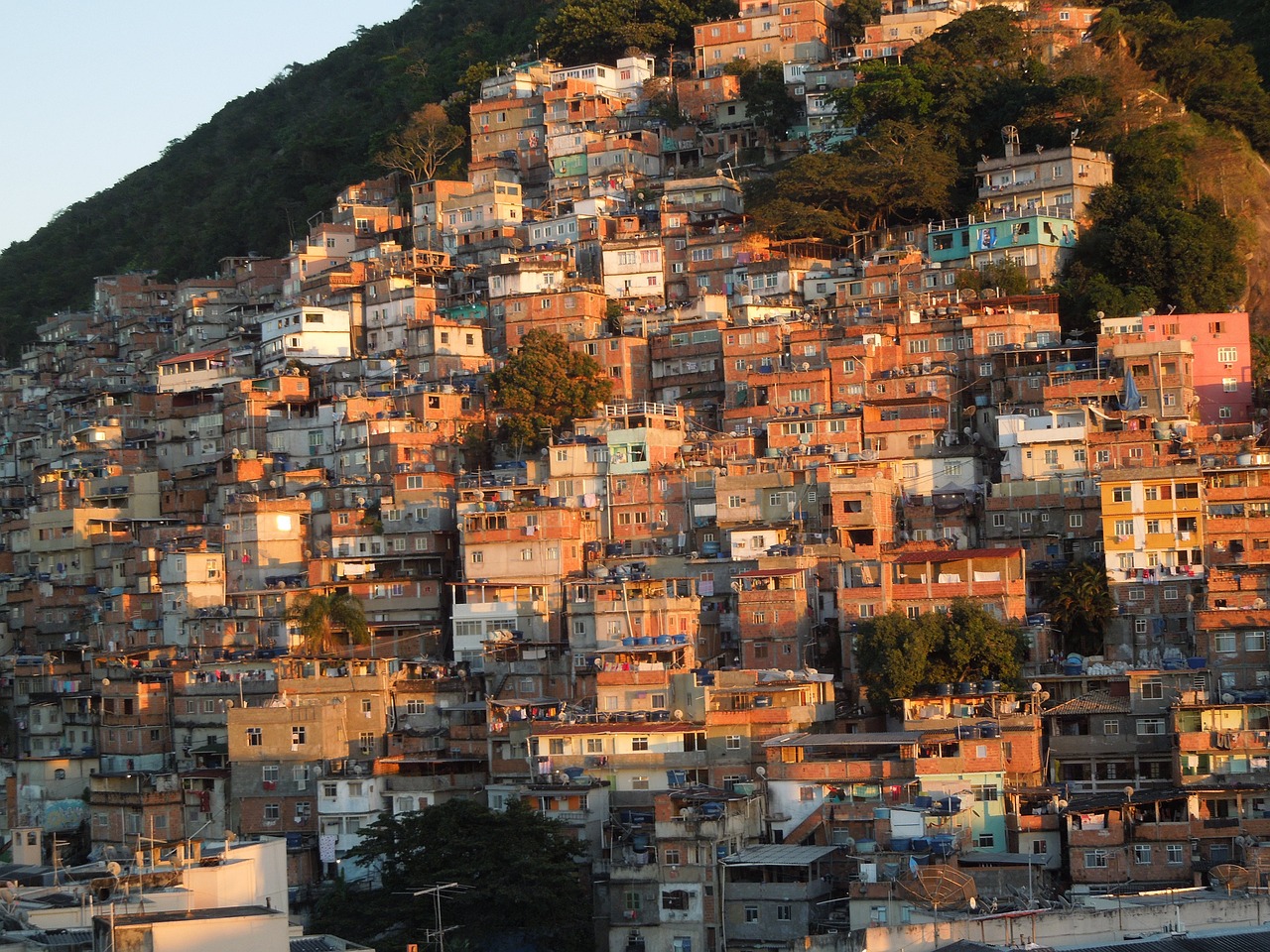

New Paper “Crime-associated inequality in geographical access to education: Insights from the municipality of Rio de Janeiro”
To what extent does crime potentially inhibit geographical access to schools, measured by cumulative average travel time? Education is recognized globally as a fundamental human right and essential for promoting equality,eradicating poverty, reducing crime, and supporting sustainable development. Despite global progress, full educational access remains a challenge, particularly in highly criminal areas. The paper uses…
-
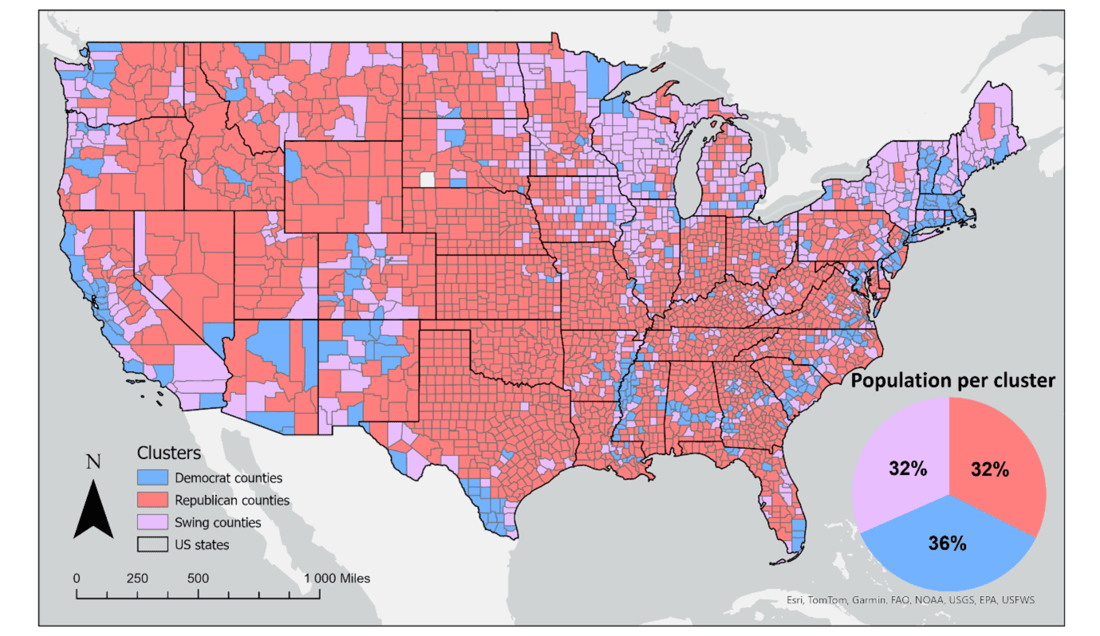
New Paper “Geosocial Media’s Early Warning Capabilities Across US County-Level Political Clusters: Observational Study”
The novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) generated significant health concerns worldwide, leading policymakers and health care experts to implement nonpharmaceutical public health interventions to mitigate the spread of the virus. While these interventions played a crucial role in controlling transmission, they also resulted in substantial economic and societal costs, necessitating strategic deployment, particularly during periods of…
-
New paper “Leveraging geospatial data to evaluate women’s employment opportunities in the renewable energy sector”
The renewable energy (RE) sector is a cornerstone of global climate action, yet its workforce remains marked by gender inequality. Women are significantly underrepresented, often relegated to lower-paid, non-technical roles. Traditional analyses of this disparity frequently ignore the spatial dimensions that influence women’s employment opportunities—factors like public transportation access, safety, and neighborhood walkability. Addressing these…
-
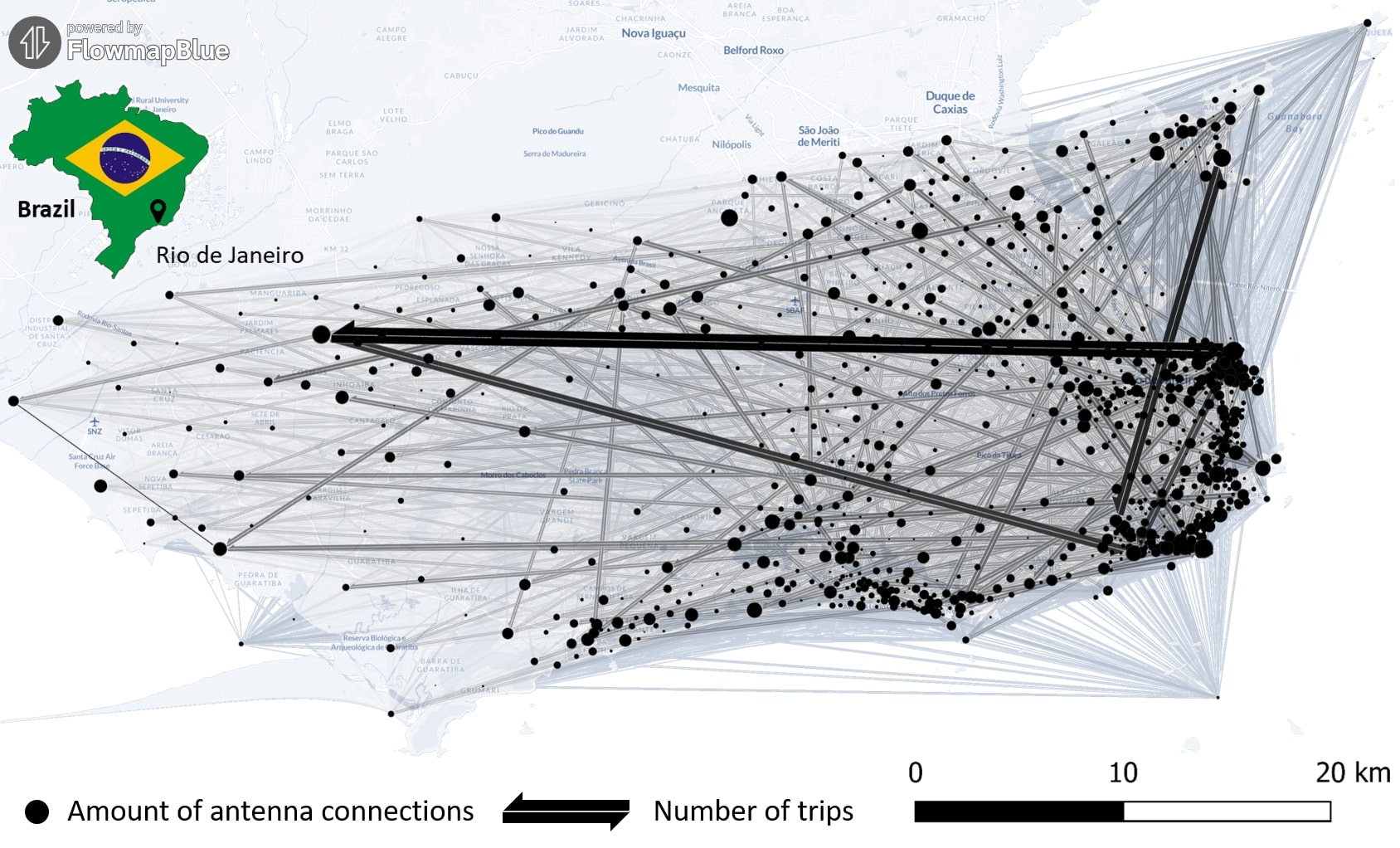
New Paper “Long-term validation of inner-urban mobility metrics derived from Twitter/X”
Data on mobility behavior can yield valuable insights that are beneficial for various applications such as public policy, emergency response, and urban planning. As the availability of freely-accessible mobility data is limited, the attention to X (formerly known as Twitter) as a data source has increased. Users of the platform can tag their online posts…
-

New Paper: GeoAI for Science and the Science of GeoAI
GeoAI integrates AI, geospatial big data, and high-performance computing for solving data- and computation-intensive geospatial problems. This field has gained continuous momentum, driven by strong demands in geography and the rapid advancement of AI. Wenwen Li´s paper “GeoAI for Science and the Science of GeoAI”, published in the latest edition of the Journal of Spatial…