Recently some of our work on intrinsic VGI quality analysis has been published. In this work we propose a framework to assess the quality of OSM building footprints data without using any reference data. More specifically, the OSM history data will be examined regarding the development of attributes, geometries and positions of building footprints. In total seven quality indicators are defined for the intrinsic quality assessment.
In terms of completeness:
(i) the development of built-up area over time,
(ii) the development of building count over time,
(iii) the development of positional accuracy attributes over time,
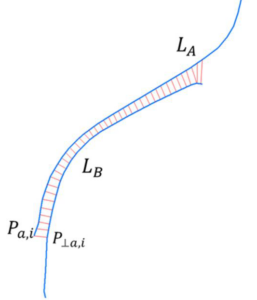
(iv) the average vertex displacement of a building footprint when edited by OSM contributors,
and in terms of shape accuracy:
(v) the orthogonality of building footprints,
(vi) the parallelism of building footprint edges to the nearby line segments of roads, and
(vii) the fragmentation of patterns formed by building footprints.
For our case study in the federal state of Baden-Württemberg (BW), Germany, a database is established based on a spatiotemporal data model which can track both individual objects and editing events on OSM. The preliminary experiments show that the quality of building footprints in BW is relatively high. And the quality in terms of semantics, geometries and positions are getting increasingly high over the time thanks to the considerable contribution of OSM volunteers.
Fan, H. A. Yang, A. Zipf (2016): Intrinsic OSM data quality assessment – The intrinsic quality assessment of building footprints data on OpenStreetMap in Baden- Württemberg. In: G. Meinel, D. Förtsch, S. Scharz, T. Krüge(eds.) Flächennutzungsmonitoring VIII Flächensparen-Ökosystemleistungen-Handlungsstrategien. RHOMBOS, pp.253-260.
IntrisicOSMquality DFG project
Selected earlier work:
Barron, C., Neis, P. & Zipf, A. (2013): A Comprehensive Framework for Intrinsic OpenStreetMap Quality Analysis. , Transactions in GIS, 18(6), 877-895. DOI: 10.1111/tgis.12073.
Dorn, H., Törnros, T. & Zipf, A. (2015): Quality Evaluation of VGI using Authoritative Data – A Comparison with Land Use Data in Southern Germany. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. Vol 4(3), pp. 1657-1671, doi: 10.3390/ijgi4031657
Fan H., Zipf A., Fu Q. and Neis P. 2014. Quality assessment for building footprints data on OpenStreetMap. In: International Journal of Geographical Information Science. DOI: 10.1080/13658816.2013.867495
Fan, H., Zipf, A. & Fu, Q. (2014): Estimation of building types on OpenStreetMap based on urban morphology analysis. AGILE Conference 2014, Castellón, Spain, Springer Lecture Notes in Geoinformation and Cartography, “Connecting a Digital Europe through Location and Place”.
Fan, H., A. Zipf and H. Wu (2016): Detecting repetitive structures on building footprints for the purpose of 3D modeling and reconstruction. International Journal of Digital Earth (IJDE). 1-13. dx.doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2016.1252433.
Goetz, M. and A. Zipf (2013): The Evolution of Geo-Crowdsourcing: Bringing Volunteered Geographic Information to the Third Dimension In: Sui, D.Z., Elwood, S. and M.F. Goodchild (eds.), 2012. Volunteered Geographic Information, Public Participation, and Crowdsourced Production of Geographic Knowledge. Berlin: Springer.
Ballatore, A. and Zipf, A. (2015): A Conceptual Quality Framework for Volunteered Geographic Information. COSIT – CONFERENCE ON SPATIAL INFORMATION THEORY XII. October 12-16, 2015. Santa Fe, New Mexico, USA. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 1-20.
Törnros, T., Dorn, H., Hahmann, S., and Zipf, A. (2015): Uncertainties of completeness measures in OpenStreetMap – A Case Study for buildings in a medium-sized German city, ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci., II-3/W5, 353-357, doi:10.5194/isprsannals-II-3-W5-353-2015.
Acknowledgements: we thank the Klaus-Tschira Foundation (KTS) and the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) for partial support of this work.