The HeiGIT gGmbH (Heidelberg Institute for Geoinformation Technology) team has just released a version 2.0 of the Sketch Map Tool, a low-tech solution for participatory sketch mapping through offline data collection, digitization and georeferencing of local spatial knowledge. Thanks to continuous support from the German Red Cross and financial support by the German Federal Foreign Office, the HeiGIT tool has undergone significant enhancements. These updates introduce new features aimed at broadening the tool’s accessibility to a wider audience, particularly non-experts.
This release is proudly dubbed “Juling,” honoring the steadfast support of Prof. Dr. Wilfried Juling in fostering the growth and advancement of HeiGIT.
The significance of incorporating local knowledge through community and interest group involvement becomes especially pronounced during the preparation for natural disasters and in the long-term planning of cities and projects. The spatial dimension plays a crucial role, and the Sketch Map Tool addresses this need by facilitating the mapping of local perceptions on paper-based maps, known as Sketch Maps. It can be particularly useful for identifying areas susceptible to flooding or drought, pinpointing critical infrastructure and civil facilities within vulnerable zones, and flagging inadequate constructions. It can help in unveiling underlying risk factors such as environmental degradation. Beyond that, the tool can be used to visualize, communicate, and deliberate on aspirations and visions, while simultaneously fostering community engagement and enhancing the usability of gained results.
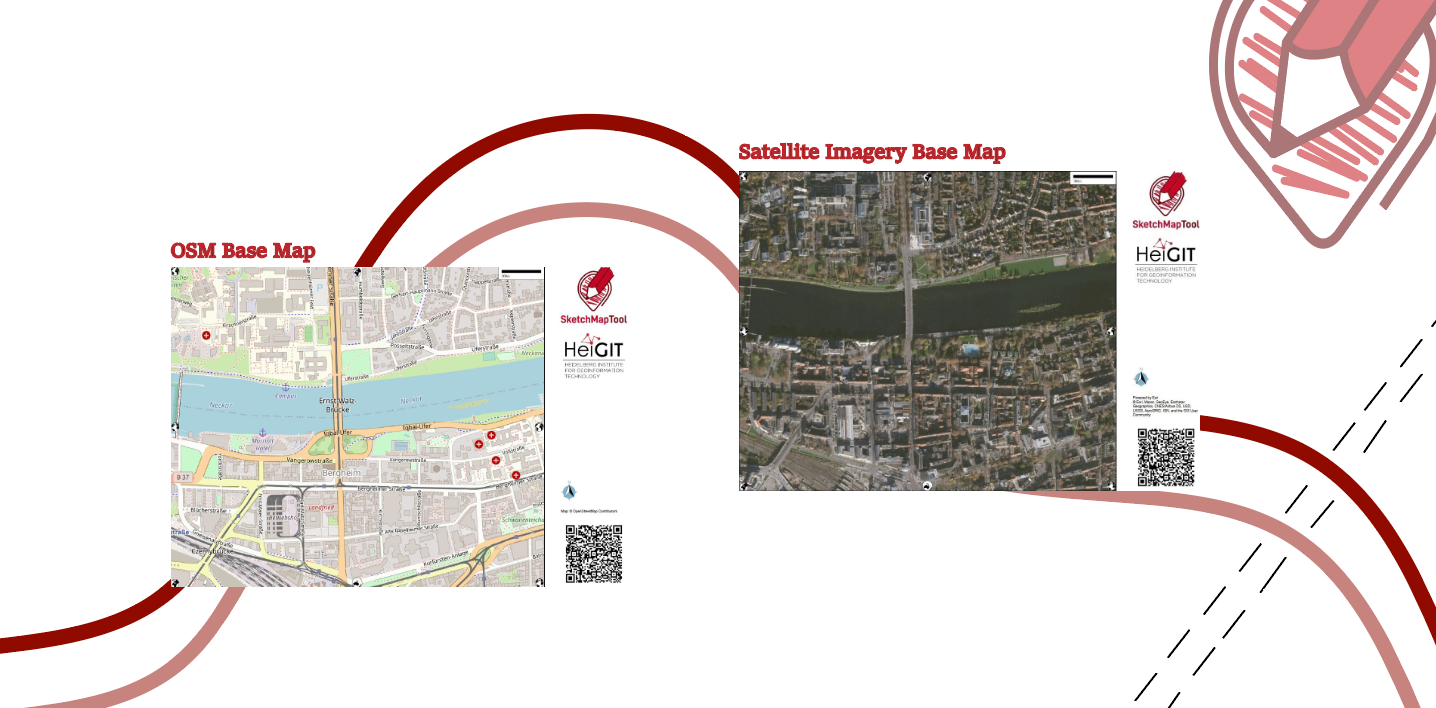
Every Sketch Map contains a basemap with OpenStreetMap data or satellite imagery, which provides a scale and orientation. Upon uploading pictures of marked maps, the tool automatically digitizes and georeferences the markings, making it downloadable for integration into Geographic Information Systems (GIS). The Sketch Map Tool bridges the gap between widely used, analogue mapping and digital analysis.
Satellite Images as Base Maps
In this latest release, one of the most requested features by our users from humanitarian organizations has been implemented—a base map layer with satellite imagery. This addition marks a significant advancement in the tool’s capabilities, catering to the needs of users, for instance, engaged in mapping within natural environments.
Satellite imagery broadens the tool’s applications, allowing for an in-depth exploration of risk drivers, including population growth, land use processes, patterns, and ecosystem services depletion. It’s particularly beneficial in areas with limited OpenStreetMap (OSM) data, aiding users unfamiliar with traditional map reading.
Furthermore, satellite imagery provides valuable insights into vegetation and topography, essential for hazard mapping in Enhanced Vulnerability and Capacity Assessment (EVCA) contexts, where local, accurate and timely data in high resolution is essential for effective decision-making. We source our satellite imagery from ESRI world imagery for quality and reliability.
Having both, satellite and OSM basemaps, offers versatility depending on the mapping area and focus. When mapping heat stress in cities, for example, OSM base maps with hospital labelling complement the satellite images showing tree coverage. In areas with dense forest cover, the use of both basemaps improves understanding.
However, disparities may arise due to differences in data currency. While edits and changes in the OSM data are immediately available and therefore an up-to-date map can be created, satellite imageries are usually 3 to 5 years old.
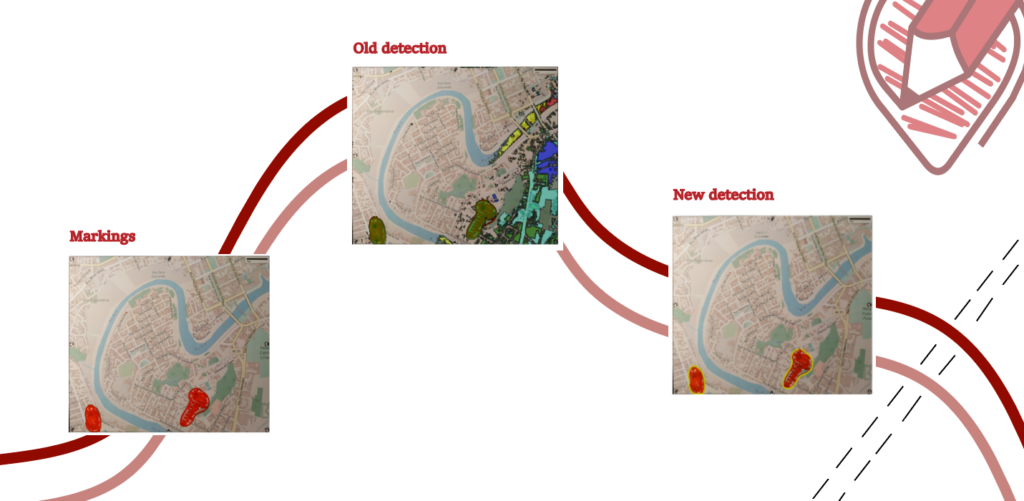
Improved Marking Detection
The new version of the Sketch Map Tool utilizes advanced Deep Learning models specifically trained to analyze Sketch Maps in order to identify marked objects. These models learn to distinguish markings from the background through supervised learning on labeled image datasets. By analyzing patterns and features, they can accurately detect and differentiate markings. This predictive capacity enables the models to identify markings in new and unseen Sketch Maps.
The tool also employs conventional Computer Vision techniques to accurately position the Sketch Map within real-world coordinates. Precise spatial alignment is acquired by detecting and matching key points, such as globes, between reference and input images. However, some problems with very dark satellite images may still occur.
Translation
With the 2.0 version, the Sketch Map Tool website will at first be available in English and German, with French and Spanish following soon, enhancing user-friendliness for non-English speakers.
Exercises for Trainers
Our new training platform offers five different exercises to explore the Sketch Map Tool and sketch mapping in general. These exercises are designed for workshop settings, allowing participants to discuss their experiences together. The Material is provided in English: Sketch Map Tool Training — GIS Resource Training Center
Want to know more?
The Sketch Map Tool launch:
We would be delighted to have your presence at the upcoming launch event scheduled for Tuesday, April 16th. The event will feature two online presentations lasting approximately 1 hours each, designed to accommodate various time zones. These presentations will focus on the Sketch Map Tool, introducing its latest features and showcasing new functionalities through examples. The sessions will conclude with an engaging Q&A session, providing you with the opportunity to interact and address any queries you may have. We look forward to your participation!
When: April 16: 1st Session 9am, 2nd Session 5 pm (UTC+2).
Where:
Join zoom meeting Launch 2024 Session 1
Join zoom meeting Launch 2024 Session 2
Fachtagung Katastrophenvorsorge:
Join us at our Workshop “Lokales Wissen kartieren mit dem Sketch Map Tool- Potentiale und Herausforderungen des partizipativen Kartierens” at the conference “Fachtagung Katastrophenvorsorge“ on Disaster Risk Reduction. The conference is dedicated to the challenges, opportunities and current developments in disaster prevention and management in the context of current national and global developments such as climate change, health crises and social and geopolitical tensions.
When: April 22 and 23, 2024
Where: Tagungswerk Berlin, Lindenstraße 85 and online