ER3DS makes cities smarter by emission reduction using 3D spatial sensing and analysis
In the new project on Emission Reduction in Smart Cities Using 3D Spatial Sensing and Analysis (ER3DS) the combination of energy modeling, highly detailed 3D geographic sensing and computation will allow us to reveal a completely new picture of the current energy situation in a city and how the potential of future emission reduction is distributed in space and time.
Renewable energy is a very important issue in the vision of smart city, especially applying the photovoltaic panels on the roof or façade of the building for the energy creation and carbon dioxide emissions reduction. Complex and dynamic shading effects on the building envelop can be accounted for using state-of-the-art 3D city models in order to calculate the hourly solar potential through the year in a dense urban area. Upscaling the computation to a city scale is, however, a demanding challenge as the preparation of 3D city model and ingenious computation algorithm need an efficient solution in terms of accuracy and computation efforts. As of now, there lacks 3D solar potential computation and carbon dioxide reduction on a city scale of more than 1 million inhabitants.

The main aim of this project is to integrate the knowledge of highly detailed 3D spatial sensing and analysis, building energy use, and urban climate from the Taiwan and Germany academics, to incorporate with SMEs and government authorities, and to promote the Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) by joint scientific initiatives and events.
ER3DS is a joint project between the National Cheng Kung University (NCKU) in Taiwan (Prof. Wang and Prof. Lin) and the 3DGeo Research Group (Prof. Bernhard Höfle). Moreover, third parties both from Germany and Taiwan are involved and can be found on the project website. The project will focus on using highly detailed 3D city models obtained from airborne and UAV-borne laser scanning data by a sophisticated raytracing algorithm, implemented in the Heidelberg’s open source research software VOSTOK (Voxel Octree Solar Toolkit). Further advancement will be achieved by integrating meteorological data (Central Weather Bureau CWB of Taiwan and Deutscher Wetterdienst DWD of Germany). A more realistic PV potential will be computed by considering the building regulation for the roof and attached facilities which are differently implemented in Germany and Taiwan.
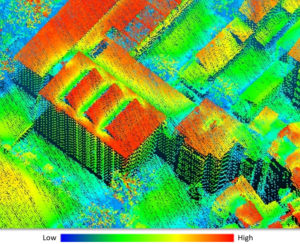
Our novel methodological approach is an important component for a universal smart city infrastructure. The result of our project is a flexible smart city service that can update the emission reduction estimations continuously.
Check out a more detailed description of ER3DS on the project website and stay tuned for latest news!
You might also be interested in reading joint publications of prior collaborations between Taiwan and Germany:
- Lin, T.-P., Lin, F.-Y., Wu, P.-R., Hämmerle, M., Höfle, B., Bechtold, S., Hwang, R.-L., &Chen, Y.-C. (2017): Multiscale analysis and reduction measures of urban carbon dioxide budget based on building energy consumption, Energy and Buildings, Vol. 153, 356-367
- Hämmerle, M., Lukač, N., Chen, K.-C., Koma, Zs., Wang, C.-K., Anders, K., & Höfle, B. (2017): Simulating various terrestrial and UAV LiDAR scanning configurations for understory forest structure modelling, ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, IV-2/W4, 59-65
- Lin, T.P., Chen, Y.C., & Matzarakis, A., 2017, Urban thermal stress climate mapping: Combination of long-term climate data and thermal stress risk evaluation, Sustainable Cities and Society,34, 12-21