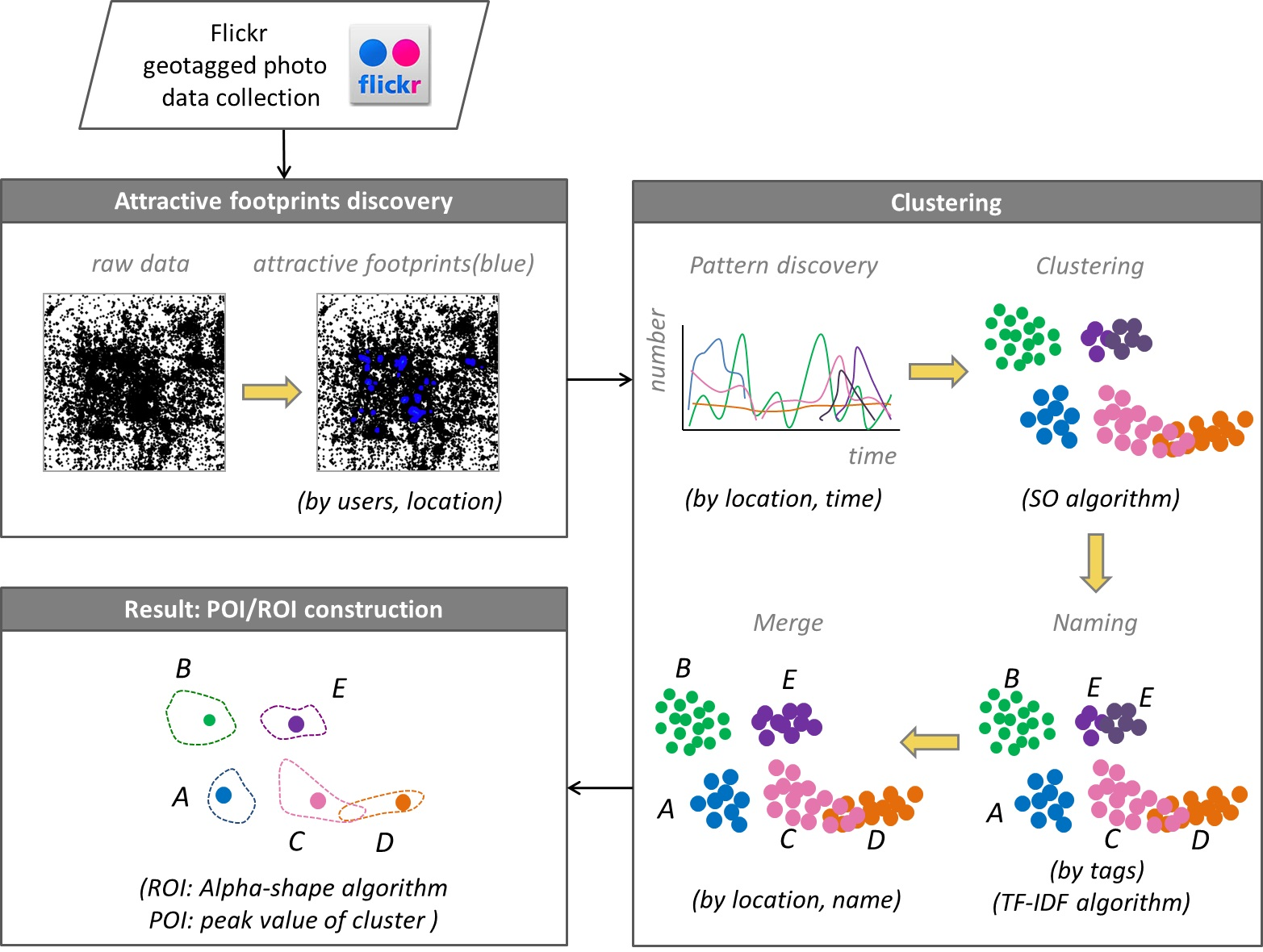
In the era of big data, ubiquitous Flickr geotagged photos have opened a considerable opportunity for discovering valuable geographic information. Point of interest (POI) and region of interest (ROI) are significant reference data that are widely used in geospatial applications. A recently published study (Kuo et al 2018) study aims to develop an efficient method for POI/ROI discovery from Flickr. Attractive footprints in photos with a local maximum that is beneficial for distinguishing clusters are first exploited. Pattern discovery is combined with a novel algorithm, the spatial overlap (SO) algorithm, and the naming and merging method is conducted for attractive footprint clustering. POI and ROI, which are derived from the peak value and range of clusters, indicate the most popular location and range for appreciating attractions. The discovered ROIs have a particular spatial overlap available which means the satisfied region of ROIs can be shared for appreciating attractions. The developed method is demonstrated in two study areas in Taiwan: Tainan and Taipei, which are the oldest and densest cities, respectively.
Our major contributions are three-fold.
- An efficient method of eliminating noises among collected footprints and selecting attractive footprints with a local maximum for delineating POIs and ROIs is proposed.
- An effective clustering toward pattern discovery that involves spatial and temporal properties and attributes, such as tags, with a spatial overlap (SO) algorithm is exploited. The discovered ROIs are particularly spatial overlap available that the satisfied region of ROIs can be shared for appreciating attractions.
- A POI and an ROI with peak value that indicate the most popular location and range for appreciating attractions, respectively, are uncovered
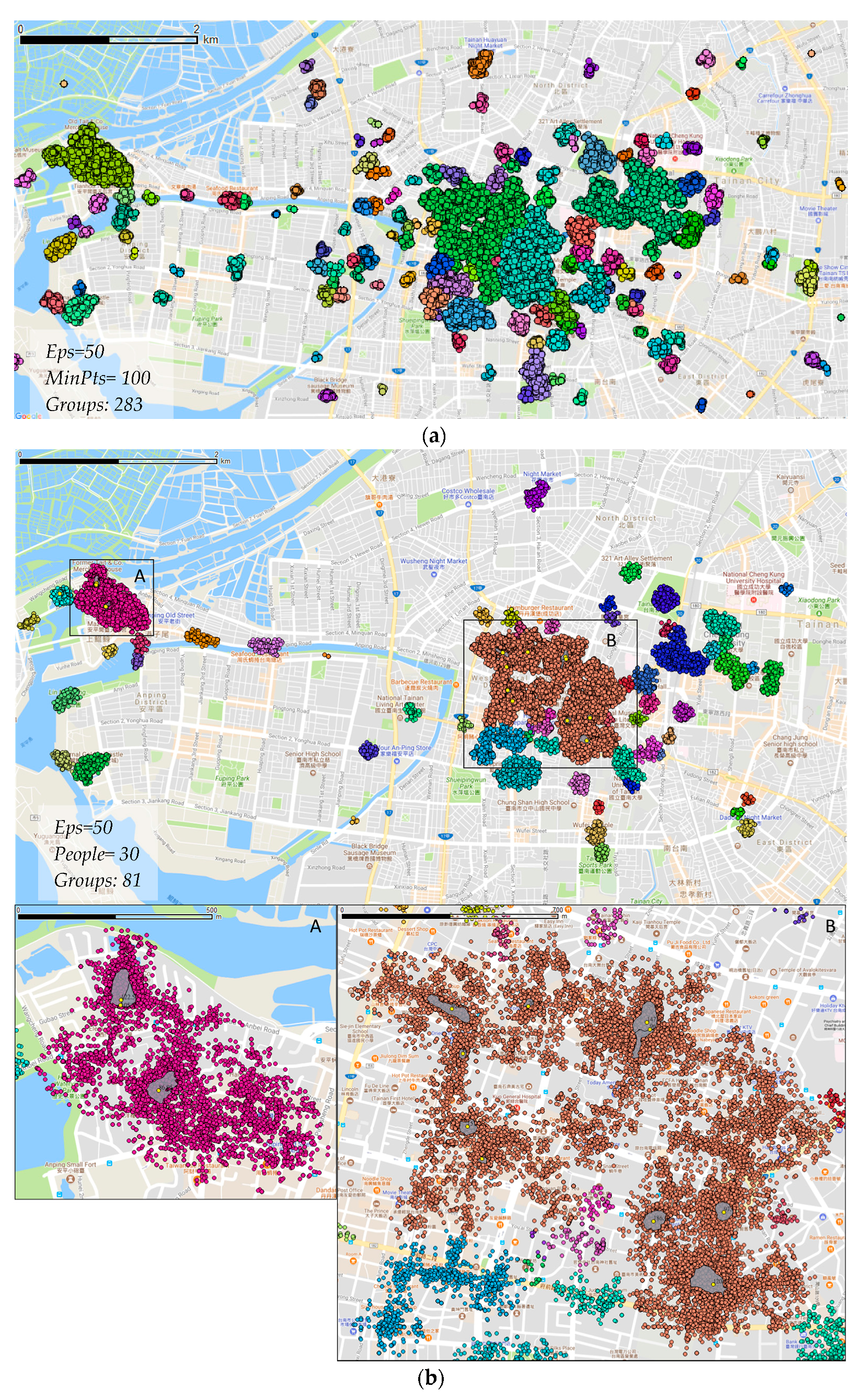
Results show that the discovered POI/ROIs nearly match the official data in Tainan, whereas more commercial POI/ROIs are discovered in Taipei by the algorithm than official data. Meanwhile, our method can address the clustering issue in a dense area.
Kuo, C.-L., T.C. Chan, I.-C. Fan, A. Zipf (2018): Efficient Method for POI/ROI Discovery Using Flickr Geotagged Photos. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7(3), 121; doi:10.3390/ijgi7030121.
Related selected earlier Work:
- Novack T., R. Peters and A. Zipf (2018): Graph-Based Matching of Points-of-Interest from Collaborative Geo-Datasets. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7(3), 117; doi:10.3390/ijgi7030117
- Westerholt, R., Steiger, E., Resch, B. and Zipf, A. (2016): Abundant Topological Outliers in Social Media Data and Their Effect on Spatial Analysis. PLOS ONE, 11 (9), e0162360. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0162360.
- Jonietz, D., Zipf, A. (2016,): Defining fitness-for-use for crowdsourced points of interest (POI). ISPRS Internat. Journal of Geo-Information. 2016. 5(9), 149; DOI:10.3390/ijgi5090149
- Rousell A. and Zipf A. (2017): Towards a landmark based pedestrian navigation service using OSM data. International Journal of Geo-Information, ISPRS IJGI, 6(3): 64.
- Yan, Y., M. Eckle, C.-L. Kuo, B. Herfort, H. Fan and A. Zipf (2017): Monitoring and Assessing Post-Disaster Tourism Recovery Using Geotagged Social Media Data. International Journal of Geo-Information, ISPRS IJGI. 6(5), 144; doi:10.3390/ijgi6050144
- Li, M., Westerholt, R., Fan, H., Zipf, A. (2016): Assessing spatiotemporal predictability of LBSN: A case study of three Foursquare datasets. GeoInformatica. Volume and issue pending. DOI:10.1007/s10707-016-0279-5.
- Steiger, E., Westerholt, R., Resch, B. and Zipf, A. (2015): Twitter as an indicator for whereabouts of people? Correlating Twitter with UK census data. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems (CEUS), 54, pp. 255–265. Elsevier. doi:10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2015.09.007
- Steiger, E., Resch, B., Zipf, A. (2015): Exploration of spatiotemporal and semantic clusters of Twitter data using unsupervised neural networks. International Journal of Geographical Information Science (IJGIS), Taylor & Francis. doi:10.1080/13658816.2015.1099658
- Steiger, E.; Porto de Albuquerque, J.; Zipf, A. (2015): An advanced systematic literature review on spatiotemporal analyses of Twitter data. Transactions in GIS, 19(6): 809–834. Wiley. doi:10.1111/tgis.12132
- Sun, Y., Fan, H., Bakillah, M. & Zipf, A. (2013): Road-based Travel Recommendation Using Geo-tagged Images. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems (CEUS). Volume 53, Pages 110-122. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2013.07.006